The Rising Tide: Why Consumers Will Use Fintech Apps More Than Ever
The fintech industry has revolutionized traditional financial services by leveraging technology to offer innovative solutions that are more accessible, efficient, and user-friendly. As digital transformation continues to permeate various aspects of life, consumers are increasingly turning to fintech apps to manage their financial activities. Let’s look into the reasons behind the growing popularity of fintech apps andthe implications for consumers and the financial industry.
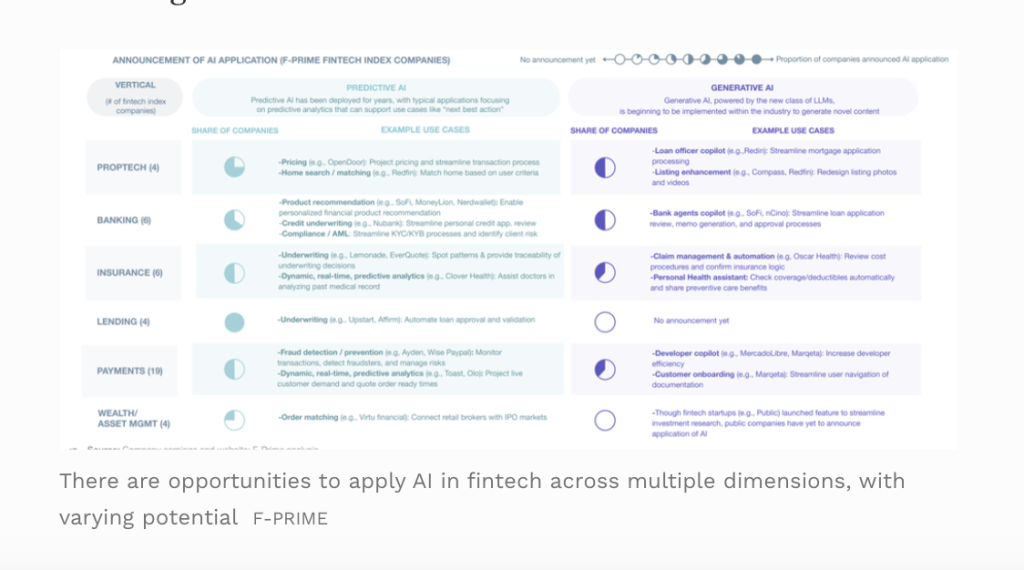
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have become pivotal in developing smart financial solutions. These technologies enable fintech apps to offer personalized financial advice, predictive analytics, and automated services. For instance, AI-driven chatbots provide 24/7 customer support, while ML algorithms analyze spending patterns to offer tailored budgeting tips.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology ensures secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transactions. Its decentralized nature reduces the risk of fraud and enhances trust in financial systems. Fintech apps utilizing blockchain can facilitate cross-border payments, streamline supply chains, and offer decentralized finance (DeFi) services, attracting a broader user base.
Enhanced Mobile Connectivity
The proliferation of smartphones and high-speed internet has made mobile banking and fintech apps more accessible than ever. Enhanced mobile connectivity allows users to perform financial transactions on the go, check account balances, and receive real-time notifications, contributing to the widespread adoption of fintech solutions.
Convenience and Accessibility
Modern consumers demand convenience and instant access to financial services. Fintech apps cater to these expectations by providing a seamless user experience, enabling users to complete transactions, apply for loans, or invest with just a few taps on their smartphones.
Personalization and Customer Experience
Fintech apps leverage data analytics to offer personalized services, such as customized investment portfolios and tailored financial advice. This level of personalization enhances customer satisfaction and fosters loyalty, as users feel that their unique financial needs are being met.
Financial Inclusion
Fintech apps play a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion by providing access to financial services for underserved populations. Mobile banking apps, microfinance platforms, and peer-to-peer lending services help individuals in remote areas or with limited access to traditional banking services participate in the financial system.
Digital Payments and Contactless Transactions
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift towards digital payments and contactless transactions. Fintech apps facilitate various payment methods, including mobile wallets, QR code payments, and peer-to-peer transfers, making it easier for consumers to transact without physical contact.
Online Banking and Financial Management
Online banking apps offer a range of services, from basic account management to advanced financial planning tools. Users can track their spending, set savings goals, and receive insights into their financial health, all through a single app.
Investment and Wealth Management
Fintech apps democratize investment and wealth management by providing access to a wide array of investment options, including stocks, bonds, cryptocurrencies, and robo-advisors. These platforms often have lower fees and minimum investment requirements, making investing more accessible to a broader audience.
Improved Financial Literacy and Empowerment
Fintech apps often include educational resources and tools that help users understand financial concepts and make informed decisions. By empowering consumers with knowledge, these apps contribute to better financial management and planning.
Cost Efficiency and Savings
Fintech solutions are typically more cost-effective than traditional financial services. Lower operational costs, reduced need for physical branches, and streamlined processes result in savings that are often passed on to consumers through lower fees and better rates.
Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
Advanced security features, such as biometric authentication, encryption, and real-time fraud detection, make fintech apps a secure option for managing finances. Continuous improvements in security protocols help protect users’ data and financial assets from cyber threats.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
As fintech apps handle sensitive financial data, ensuring data privacy and security is paramount. Users must trust that their information is protected, and companies need to adhere to strict data protection regulations to prevent breaches and misuse of data.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
The fintech industry is subject to a complex regulatory landscape that varies by region. Navigating these regulations can be challenging for fintech companies, and non-compliance can result in hefty fines and legal issues.
Technological Barriers and Digital Divide
While fintech apps have made financial services more accessible, there remains a digital divide that prevents some populations from benefiting. Limited access to smartphones, internet connectivity, and digital literacy are significant barriers that need to be addressed to ensure inclusive growth.
The fintech sector is poised for continued growth as consumers increasingly turn to digital solutions for their financial needs. Technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and evolving financial landscapes are driving this trend, offering numerous benefits while also presenting challenges that need to be managed. As fintech apps become more integrated into daily life, their impact on financial services and consumer behavior will only intensify, shaping the future of finance.



